
There are different types of SaaS business models, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Software-as-a-service (SaaS) sector has undergone exponential growth since it burst onto the scene in 2005. SaaS businesses are becoming increasingly popular for a variety of reasons. They are typically more affordable than purchasing traditional software and easy to use. Massive amounts of time and capital are currently going into SaaS companies and businesses, which stand a strong chance of succeeding if they fulfill market demands.
In this article, we will explore the most common models and SaaS business model examples of the most successful businesses.
What is a SaaS Business?
Software as a service (SaaS) is the practice of offering consumers cloud-based software. It is a way of distributing and licensing software in which the product is accessed online through a monthly/yearly subscription rather than being purchased and installed on specific PCs.
A SaaS business is a type of business model where software is provided to customers on a subscription basis. Customers can access the software remotely, typically through the internet.
SaaS businesses are usually hosted on the cloud, providing scalability and flexibility for the company and the customer. The term “cloud” simply refers to the area of the internet where businesses have developed their resource infrastructure and where they allot some of these resources to new customers.
Similarly to other business models, SaaS also has its positive sides and drawbacks. Keep reading to discover the advantages and disadvantages of a SaaS business model.
Advantages of a SaaS Business Model

- Scalability. The cloud-based infrastructure of a SaaS business makes it easy to scale up or down as needed. This means that SaaS businesses can respond quickly to changes in customer demand.
- Recurring revenue. Because customers pay monthly or yearly, SaaS businesses have a steadier stream of income than companies that rely on one-time sales. This can make it easier to predict and plan for growth.
- Easier pivoting and modification. SaaS businesses can modify their offerings quickly and easily in response to customer feedback or changes in the market. This agility can be a major advantage over traditional software companies.
- More market potential. SaaS is subscription-based and available on the cloud, meaning that SaaS businesses can reach a global market more easily. Customers in any location with an internet connection can subscribe to a SaaS service.
- Loyal customer base. Since customers pay regularly, they are more likely to remain loyal to a SaaS service that they are satisfied with. This can lead to long-term relationships between the company and its customers and long-term income.
Disadvantages of a SaaS Business Model
There are also some disadvantages associated with operating a SaaS business, including:- More competition. Since the barriers to entry are relatively low, there is a lot of competition in the SaaS market. This can make it difficult for new companies to stand out from the crowd and attract customers.
- Aggressive strategy for customer retention and churn. Since SaaS businesses rely on recurring revenue, they must constantly strive to retain their customers. If a customer ends their subscription, the business loses income. As a result, SaaS businesses often have aggressive strategies for customer retention and churn prevention.
- Capital dependent. SaaS businesses require a substantial amount of initial investment to get off the ground. This can make it challenging for new businesses to get started. Also, SaaS businesses must continuously invest in their product to keep up with the competition and maintain a high level of customer satisfaction. This can be a challenge for small businesses with limited resources.
What are the different SaaS Business Models?
Now that you’re familiar with the advantages and disadvantages of a SaaS business model, let’s explore different types of SaaS business models.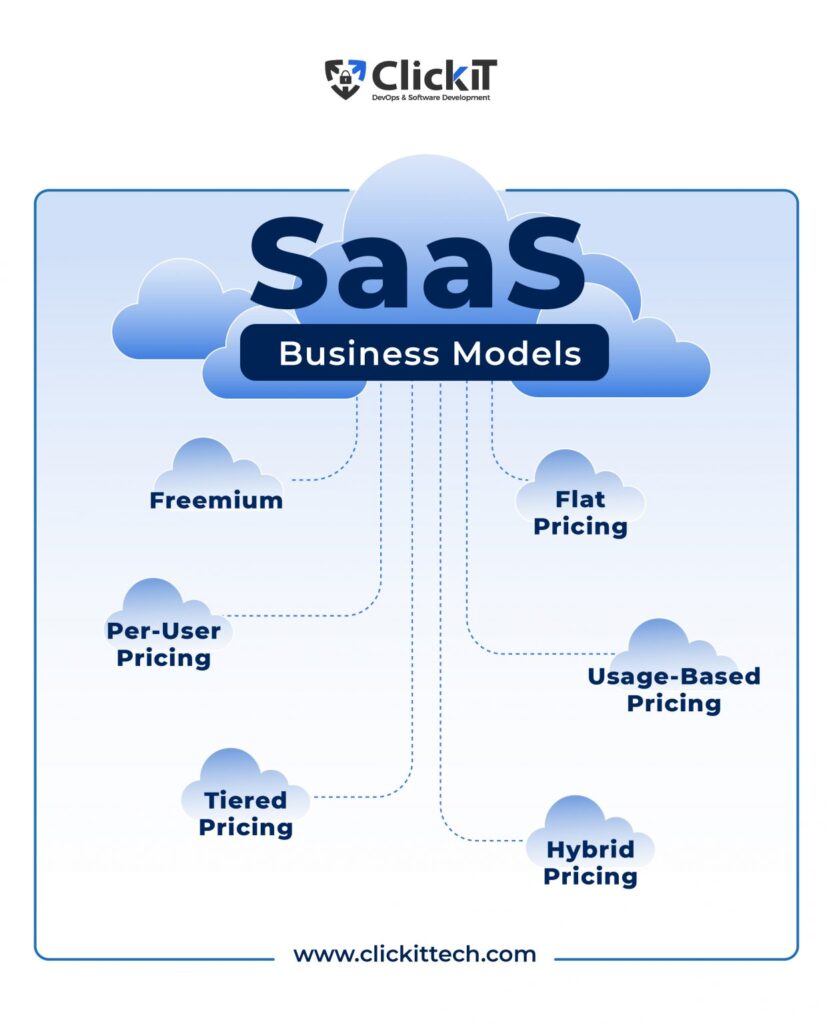
1. Freemium
The freemium model provides customers can access a basic version of the software for free. They must pay a monthly or yearly subscription fee if they want to use the advanced features.
This model is often used by companies that want to increase their customer base quickly. Providing the service for free will draw many users in. Once they use the service and see its value, they will likely pay for a more extensive set of features.
2. Flat Pricing
Under the flat pricing model, customers pay a set price for access to the software. This price is not based on usage levels or the number of users. Instead, it is a one-time or monthly/yearly subscription fee that gives the customer unlimited access to the software.
Flat pricing is simple and easy to understand, which can appeal to customers. Because the price is not based on usage, customers don’t have to worry about exceeding their budget. This predictability can make it easier for them to justify the cost of the software.
3. Usage-Based Pricing
Under the usage-based pricing model, customers are charged based on their level of usage.
This model can be appealing to customers because they only pay for what they use. If they don’t use the software often, they won’t have to pay a high price. This pricing model also gives customers the flexibility to increase their usage as their needs change.
Users often think that “pay for what you use” is a fair way to charge, and smaller companies won’t be scared away by high prices.
4. Per-User Pricing
Under the per-user pricing model, customers are charged based on the number of users that have access to the software. The price may be a monthly or yearly subscription fee.
This model is often used by businesses that need to give multiple employees access to the software. For example, a company might need to give five customer service representatives access to a customer relationship management (CRM) system.
Per-user pricing is best for situations where a lot of people need to use your software simultaneously, especially if each person needs access to different features.
5. Tiered Pricing
Under the tiered pricing model, customers are charged based on the features they use. The price may be a monthly or yearly subscription fee.
This model is often used by businesses that offer different levels of service. For example, a company might offer a basic CRM system for small businesses and a more advanced CRM system for larger businesses. The price of the advanced system would be higher because it includes more features.
6. Hybrid Pricing
The hybrid pricing model combines two or more of the other models. For example, a company might offer a basic CRM system for free and charge customers based on usage if they want to use the advanced features.
This model gives businesses the flexibility to tailor their pricing to meet the needs of their customers. It also allows businesses to try different pricing models to see what works best.
SaaS Business Models Examples
Now that you’re familiar with different SaaS business models let’s check out a few popular SaaS business model examples.
Mailchimp
Mailchimp is a SaaS company that provides online marketing tools to small businesses. The company is based on a freemium business model. This means that the customers can test out most features free of charge.
Mailchimp offers three different products to its users: the Marketing Platform, Website & Commerce, and Transactional Email. Most of Mailchimp’s clients are small businesses, but it also works with large companies. Customers can use Mailchimp to create and send email campaigns, design landing pages, and track their marketing progress.
Mailchimp offers a plan that is free of charge for customers who have up to 1,500 subscribers. For customers with more than 1,500 subscribers, Mailchimp offers multiple paid subscription plans that include different features.
Shopify
Shopify is a SaaS business model example company that provides an e-commerce platform for businesses of all sizes. Customers can use Shopify to create an online store, manage inventory, process payments, and track shipping.
Shopify has a distinct approach to its users- the company wants to do more than just sell its products to customers. It also wants to help its users become more successful by using the platform. Why? When merchants make more money, Shopify makes more money. This is also a major reason why Shopify has grown to where it is now.
The company offers different subscription plans that range from $29 to $299 per month. In other words, Shopify uses the tiered pricing SaaS model. The features included in each plan vary, but all plans include basic features such as a website builder, shopping cart, and product catalog.
Shopify also provides a 14-day trial for customers who want to test the platform before committing.
HostGator
HostGator is a SaaS business model example that provides web hosting and related services to businesses of all sizes. Customers can use HostGator to create a website, host email accounts, and manage their domain name.
The company offers different subscription plans that start at a price as low as $2.75. Similar to Shopify, HostGator uses the tiered pricing model. The features included in each plan vary slightly, but all plans include basic features such as website building tools and 24/7 customer support.
The market is quickly opened up to people with different budgets thanks to the tiered pricing strategy. Additionally, it enables new users to try out the product at the most basic level before upgrading as necessary.
HostGator also offers a 45-day money-back guarantee for customers who are not satisfied with their service.
Need Assistance with a SaaS App Development? Launch Your App with ClickIT
You can’t run a successful SaaS business even if you don’t have an accompanying app. Launch your SaaS app in time and capture the market share that your idea deserves with a proper SaaS Application Development service.
With the ClickIT team by your side, you’ll be able to cut the layers and unproductive mistakes out of your process. The ability to build SaaS Apps around various ideas for different industries is exactly what sets ClickIT apart from its competitors.
The ClickIT team completed more than 50 projects for startups and enterprises alike. Our services include:
- Multi-tenant and SaaS application architecture
- DevOps for SaaS
- AI ML SaaS app
- FinTech SaaS application
- Enterprise management SaaS solution
- SaaS platform for marketing automation
- Healthcare and patient record SaaS solution
- IoT and wearable tech SaaS applications
Conclusion
SaaS businesses have a lot of flexibility when it comes to choosing a business model. The most important thing is to choose a model that aligns with the company’s goals and objectives. If you want your SaaS business models to work, you must make a long-term commitment to customer success, including staying on top of the latest trends and technologies.
Since AI, machine learning, and data automation are becoming more popular, more businesses are looking forward to adding them to their SaaS platform. Ensure optimum customer satisfaction and stay ahead of the competitors by implementing the latest technologies into your services.
Looking to get your SaaS business off the ground? ClickIT is your choice for developing a SaaS application tailored to your specific needs!
FAQs
There are three main types of SaaS The most commonly used software-as-a-service types businesses purchase are:
-Cloud-based
-On-premises
-Hybrid.
A SaaS provider is a business that houses applications and makes them accessible to consumers online. There are many SaaS brands out there, but some of the most popular include Salesforce, HubSpot, Zendesk, and Shopify.
There are numerous SaaS business models available. Most popular are freemium, flat pricing, usage-based pricing, per-user pricing, tiered pricing, and hybrid pricing.

